HTTP Ingest (Webhook)
The HTTP Ingest connector allows you to capture data from incoming HTTP requests. A common use case is to capture webhook deliveries, turning them into an Estuary collection.
If you need to capture a dataset hosted at an HTTP endpoint, see the HTTP File connector.
Usage
This connector is different from most other capture connectors in that it's not designed to pull data from a specific system or endpoint. It requires no endpoint-specific configuration, and can accept any and all valid JSON objects from any source.
This is especially useful if you want to test out Estuary or see how your webhook data will be received.
To begin, use the web app to create and publish a capture. Estuary will create a unique URL for your public endpoint. By default, this will accept webhook requests at https://<your-public-endpoint>/webhook-data, but you can customize the path, or even capture from multiple URL paths if you like.
Webhook URLs
Some services, such as GitHub, Shopify, and Segment, allow you to send data to a specified URL. Estuary can generate and manage this destination URL. You will then need to add Estuary’s URL to the source service. This will allow the source service to send webhook data directly to your Estuary capture.
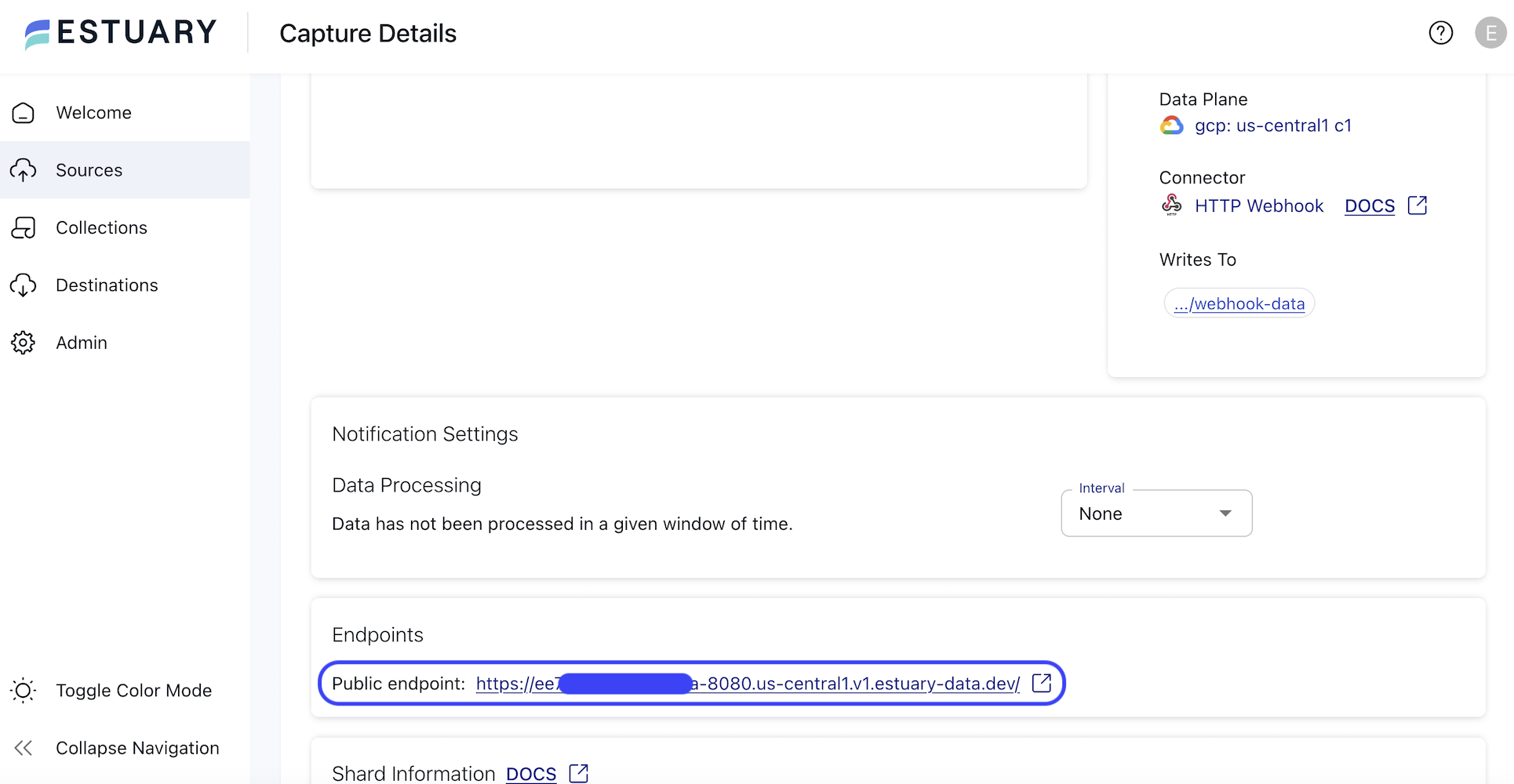
To determine the full URL:
-
Your capture must first be published and enabled.
-
Retrieve the base URL.
On the Capture Details page, scroll down to the Endpoints section. The listed link will be the base URL for your webhook. This should be something like
https://abc123-8080.us-central1.v1.estuary-data.dev. -
Add the specific path.
This will depend on the capture's
pathsendpoint configuration field. By default, this is/webhook-data. You can add additional paths topaths, and the connector will accept webhook requests on each of them.
Using this example, the full webhook URL would be: https://abc123-8080.us-central1.v1.estuary-data.dev/webhook-data
Each path will correspond to a separate binding. If you're editing the capture via the UI, click the "refresh" button after editing the URL paths in the endpoint config to see the resulting collections in the bindings editor. For example, if you set the path to /my-webhook.json, then the full URL for that binding would be https://<your-unique-hostname>/my-webhook.json.
Any URL query parameters that are sent on the request will be captured and serialized under /_meta/query/* the in documents. For example, a webhook request that's sent to /webhook-data?testKey=testValue would result in a document like:
{
"_meta": {
"webhookId": "...",
"query": {
"testKey": "testValue"
},
...
}
...
}
Send sample data to Estuary
-
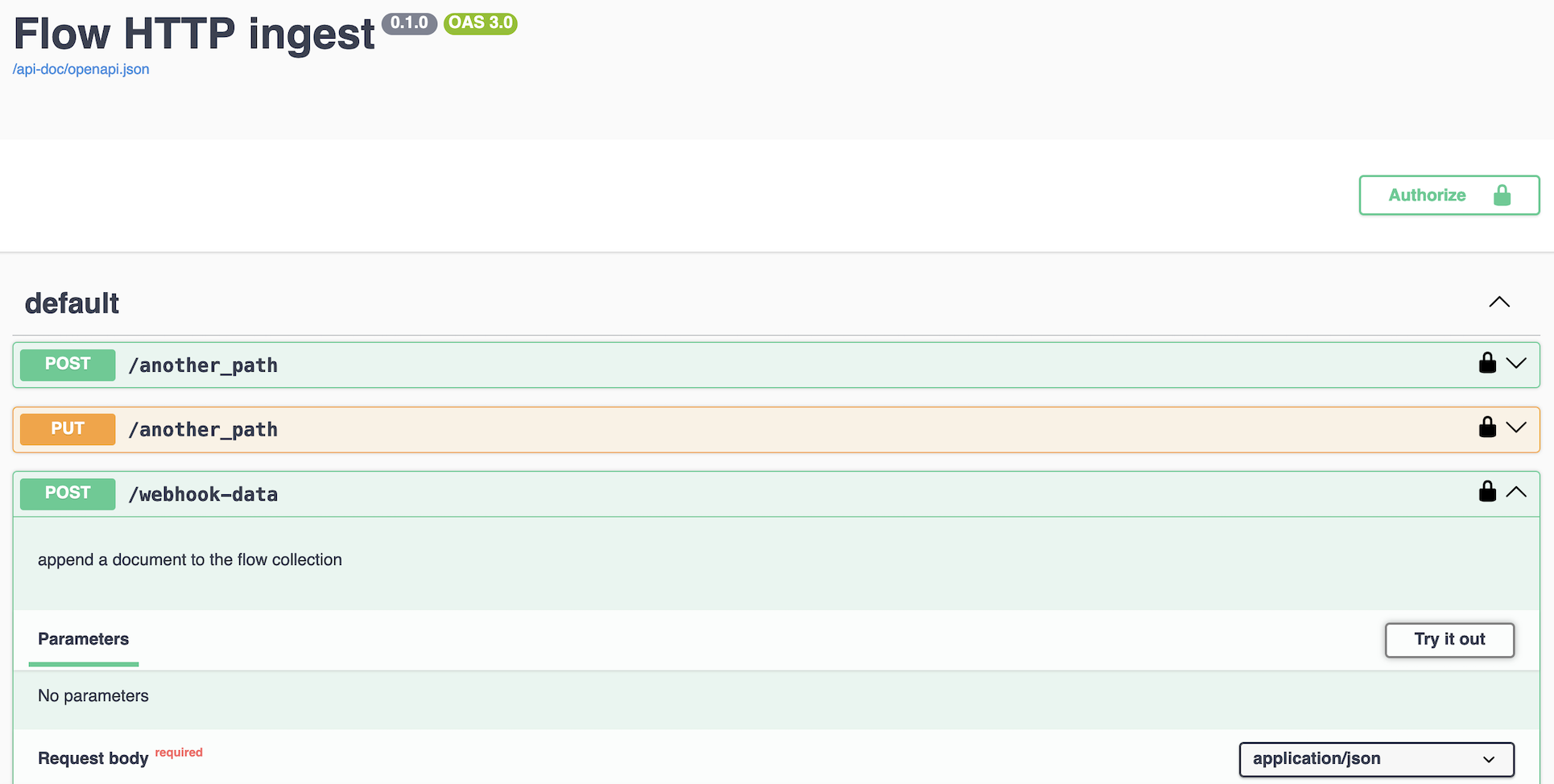
After publishing the capture, click the endpoint link from the confirmation dialog to open the Swagger UI page for your capture.
-
Expand POST or PUT and click Try it out to send some example JSON documents using the UI. You can also copy the provided
curlcommands to send data via the command line. -
After sending data, go to the Collections page of the Estuary web app and find the collection associated with your capture. Click Details to view the data preview.
Path parameters
Paths are allowed to contain parameter placeholders, which will be captured and serialized under /_meta/pathParams/* in the documents. For example, if you configure a path for /foo/{fooId} a webhook request that's sent to /foo/123 would result in a document like:
{
"_meta": {
"webhookId": "...",
"pathParams": {
"fooId": "123"
},
"reqPath": "/foo/{fooId}",
...
}
...
}
Multiple parameters are allowed, for example /foo/{fooId}/bar/{barId}. Each parameter corresponds to exactly one path segment in the request URL. Capturing multiple segments in a single parameter is not supported. The syntax and semantics of the path specification follow the OpenAPI specification (a.k.a Swagger).
Path parameters are automatically added to the collection write schema as required properties, so they can be used as part of the collection key by editing the collection during capture creation.
Care must be taken when specifying multiple paths, to ensure they don't conflict with each other. For example, you may not specify both /{paramA} and /{paramB}, because it would be impossible to determine which path to use for a request to /123.
Webhook IDs
Webhook delivery is typically "at least once". This means that webhooks from common services such as Github, Segment, Shopify, etc. may sometimes be sent multiple times.
In order to prevent problems due to duplicate processing of webhooks, these services typically provide either an HTTP header or a field within each document that serves
as a unique ID for each webhook event. This can be used to deduplicate the events in your webhook-data collection. The key of the discovered webhook-data collection is /_meta/webhookId.
By default, this value is generated automatically by the connector, and no-deduplication will be performed.
You can set the idFromHeader option in the resource configuration to have the connector automatically assign the value of the given HTTP header to the /_meta/webhookId property.
Doing so means that a materialization of the webhook-data collection will automatically deduplicate the webhook events.
Here's a table with some common webhook services and headers that they use:
| Service | Value to use for idFromHeader |
|---|---|
| Github | X-Github-Event |
| Shopify | X-Shopify-Webhook-Id |
| Zendesk | x-zendesk-webhook-id |
| Jira | X-Atlassian-Webhook-Identifier |
Custom collection IDs
Some webhooks don't pass a deduplication ID as part of the HTTP headers. That's fine, and you can still easily deduplicate the events.
To do so, you'll just need to customize the schema and key of your webhook-data collection, or bind the webhook to an existing collection that already has the correct schema and key.
Just set the key to the field(s) within the webhook payload that uniquely identify the event.
For example, to capture webhooks from Segment, you'll want to set the key to ["/messageId"], and ensure that the schema requires that property to exist and be a string.
Authentication
The connector can optionally require each request to present an authentication token as part of an Authorization: Bearer HTTP header. To enable authentication, generate a secret and paste it into the "Require Auth Token" field. We recommend using a password manager to generate these values, but keep in mind that not all systems will be able to send values with certain special characters, so you may want to disable special characters when you generate the secret. If you enable authentication, then each incoming request must have an Authorization header with the value of your token. For example, if you use an auth token value of mySecretToken, then the header on each request must be Authorization: Bearer mySecretToken.
If you don't enable authentication, then anyone who knows the URL will be able to publish data to your collection. We recommend using authentication whenever possible.
CORS allowed origins
Under Endpoint Config, you can set CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) allowed origins for your webhook URLs. By default, CORS will be disabled. Enable it by adding at least one allowed request origin to the list. Each value in the list will be permitted by the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header.
Webhook signature verification
This connector supports ECDSA P-256 signature verification for webhook providers. Verification is always disabled by default. When enabled, requests with missing or invalid signatures will be rejected with a 401 Unauthorized response.
Configuration varies by provider.
Twilio SendGrid
For Twilio SendGrid webhooks, use the streamlined configuration that only requires your verification key:
{
"signatureConfig": {
"provider": "twilio",
"publicKey": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\n...\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----"
}
}
The verification key can be found in your SendGrid Event Webhook settings.
Custom Providers
For other webhook providers that use ECDSA P-256 signatures, use the "custom" configuration to specify custom headers:
{
"signatureConfig": {
"provider": "custom",
"algorithm": "ecdsa",
"publicKey": "-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\n...\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----",
"signatureHeader": "X-Custom-Signature",
"timestampHeader": "X-Custom-Timestamp"
}
}
- provider: Set to
"custom"for custom configuration - algorithm: The signature algorithm (currently only
"ecdsa"is supported) - publicKey: PEM-encoded ECDSA P-256 public key from your webhook provider
- signatureHeader: HTTP header containing the base64-encoded DER signature
- timestampHeader: (optional) HTTP header containing the timestamp to prepend to the body before verification
If your use case requires a different verification scheme, please contact support@estuary.dev and let us know.
Handling errors and retries
The HTTP Ingest connector validates all request data against the collection's write schema. If any document in the request fails validation, the connector returns a response with an HTTP 400 status and none of the documents in that request will be captured.
The connector may occasionally return responses with HTTP 5XX status codes. This most commonly happens when the connector restarts, typically in response to a publication of the capture. These restarts are infrequent and quick (usually less than 5 seconds).
To reliably capture webhook data, the sender must retry any requests that fail with a 5XX status. Many third-party webhook senders handle retries automatically, but there are some exceptions, such as GitHub. When retrying failed webhook requests, we strongly recommend using exponential backoff with random jitter.
Recommended retry strategy:
- Use exponential backoff (e.g., 1s → 2s → 4s → 8s)
- Add random jitter to prevent thundering herd issues
- Queue failed payloads locally if all retries fail and retry later
Endpoint Configuration
| Property | Title | Description | Type | Required/Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| **** | EndpointConfig | object | Required | |
/require_auth_token | Authentication token | Optional bearer token to authenticate webhook requests. WARNING: If this is empty or unset, then anyone who knows the URL of the connector will be able to write data to your collections. | null, string | null |
/paths | URL Paths | List of URL paths to accept requests at. Discovery will return a separate collection for each given path. Paths must be provided without any percent encoding, and should not include any query parameters or fragment. | null, string | null |
/signatureConfig | Signature Verification | Configuration for verifying webhook signatures. | object | {"provider": "none"} |
Signature Config: None
| Property | Title | Description | Type | Required/Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
/signatureConfig/provider | Provider identifier | string | Required ("none") |
Signature Config: Twilio SendGrid
| Property | Title | Description | Type | Required/Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
/signatureConfig/provider | Provider identifier | string | Required ("twilio") | |
/signatureConfig/publicKey | Verification Key | PEM-encoded ECDSA public key from Twilio SendGrid Event Webhook settings. | string | Required |
Signature Config: Custom
| Property | Title | Description | Type | Required/Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
/signatureConfig/provider | Provider identifier | string | Required ("custom") | |
/signatureConfig/algorithm | Algorithm | The signature verification algorithm. | string | Required ("ecdsa") |
/signatureConfig/publicKey | Public Key | PEM-encoded public key. | string | Required |
/signatureConfig/signatureHeader | Signature Header | HTTP header containing the base64-encoded signature. | string | Required |
/signatureConfig/timestampHeader | Timestamp Header | Optional HTTP header containing the timestamp. | string | null |
Resource configuration
| Property | Title | Description | Type | Required/Default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| **** | ResourceConfig | object | Required | |
/idFromHeader | Set the /_meta/webhookId from the given HTTP header in each request. If not set, then a random id will be generated automatically. If set, then each request will be required to have the header, and the header value will be used as the value of `/_meta/webhookId`. | null, string | ||
/path | The URL path to use for adding documents to this binding. Defaults to the name of the collection. | null, string | ||
/stream | The name of the binding, which is used as a merge key when doing Discovers. | null, string |